Refrigeration Circuit With Variable Load
Product Details:
X
Product Description
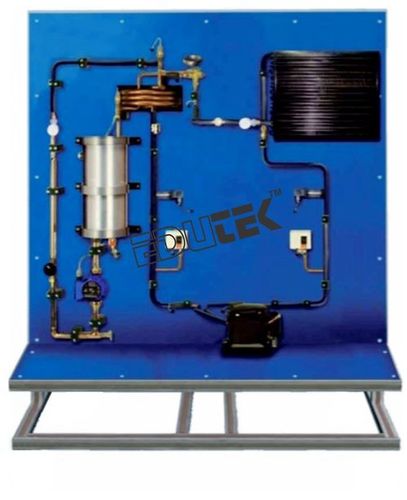
REFRIGERATION CIRCUIT WITH VARIABLE LOAD
Refrigeration systems with two-stage compression are used for the generation of particularly low temperatures. At very low temperatures large pressure differences are required between the evaporator and condenser. In a compressor the volumetric efficiency drops significantly at high pressure ratios. Therefore, two compressors are connected in series, with each compressor only having a relatively low pressure ratio. This makes a more favourable dimensioning of the low pressure stage compressor possible. Due to the large specific volume it requires a larger capacity at lower drive power. In addition, intercooling between the low pressure compressor (LP) and the high pressure compressor (HP) reduces the outlet temperature of the HP compressor to harmless values and improves the efficiency of the compression.
The unit perform the following experiments and investigations:
Learning Objectives / Experiments
- Design and components of a refrigeration system
- Compressor
- Condenser
- Thermostatic expansion valve evaporator
- Pressure switch
- Representation of the thermodynamic cycle in the
- Log p-h diagram
- Determination of important characteristic variables
- Coefficient of performance
- Refrigeration capacity
- Compressor work
- Operating behaviour under load
Specification
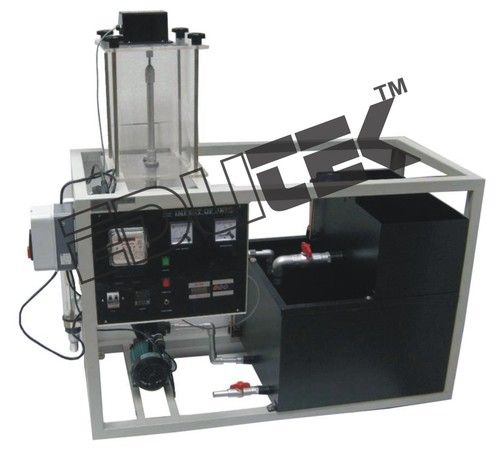
- Investigation of a refrigeration circuit with water circuit as load
- Refrigeration circuit with compressor, condenser with fan, thermostatic expansion valve and coaxial coil heat exchanger as evaporator
- Water circuit with pump, tank with heater as cooling load at the evaporator
- Heater with controller to adjust the tank temperature
- Record of all relevant measured values and display directly at the location of measurement
- Software for data acquisition via USB under Windows Vista or Windows 7
- Refrigerant R134a, CFC-free
Technical Data
- Compressor
- Refrigeration capacity: approx. 380W at 5/40°C
- Evaporator
- Refrigerant volume: 0,4L
- Water volume: 0,8L
- Condenser
- Transfer area: approx. 1,25m²
- Fan power consumption: 4x 12W
- Pump
- Max. flow rate: 1,9m³/h
- Max. head: 1,4m
- Tank
- Volume: approx. 4,5L
- Heater: approx. 450W
Measuring ranges
- Pressure: 2x -1...15bar
- Compressor power: 1x 0...750W
- Temperature: 6x 0...100°C
- Flow rate (water): 1x 0,05...1,8L/min
Dimensions and Weight
- LxWxH: 1400x560x1800mm
- Weight: approx. 138kg
Tell us about your requirement

Price:
Quantity
Select Unit
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
Additional detail
+91
Email
Other Products in 'Fluid Mechanics Lab Equipment' category
"We deal all over World but our main domestic market is South India"
 |
EDUTEK INSTRUMENTATION
All Rights Reserved.(Terms of Use) Developed and Managed by Infocom Network Private Limited. |