Energy Losses In Piping
Product Details:
X
Product Description
ENERGY LOSSES IN PIPING ELEMENTS
When water flows through a pipe system, the flow resistances causes pressure losses to occur at pipe fittings and valves and fittings.
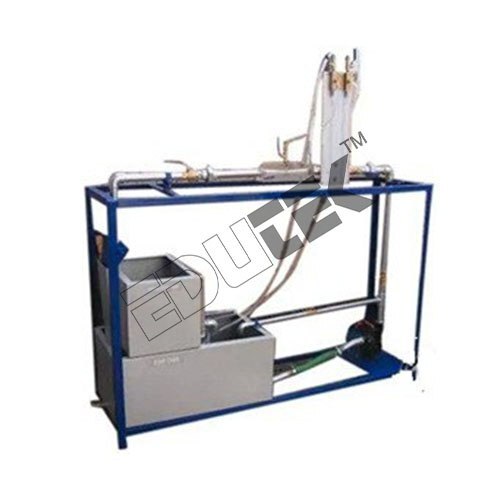
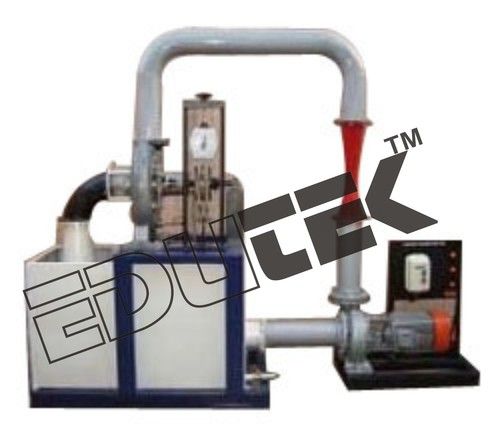
The unit can be used to investigate and visualise the pressure losses in pipe elements. The experimental unit can be used to assess how different pipe geometries affect the flow.
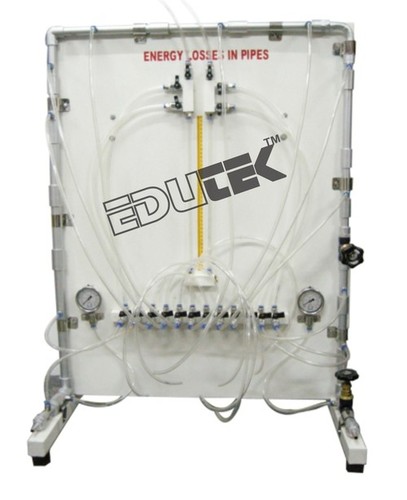
The experimental unit comprises a pipe section containing several pipe elements with different flow resistances, as well as a contraction and enlargement piece. There is also a ball valve integrated in the pipe. There are pressure measuring points with annular chambers upstream and downstream of the pipe elements, which ensure accurate pressure measurement. The pressure measuring points can be connected in pairs to a 6 tube manometers in order to determine the pressure loss of a pipe element.
The well-structured instructional material sets out the fundamentals and provides a step-by-step guide through the experiments.
Learning Objectives / Experiments
- investigate pressure losses at segment bend and bends
- Investigate pressure loss at contraction and enlargement
- Pressure loss at a ball valve and determination of a simple valve characteristic
Specification:
- Investigation of the pressure loss in flow through pipe fittings and in the ball valve
- Sudden contraction and sudden enlargement, pipe bend, segment bend, pipe angle and ball valve as measurement objects
- Annular chambers allow precise measurement of pressure
- 6 tube manometers for displaying the pressures
- Bourdon tube pressure gauge for pressure measurement
- Flow rate determined by base module
- Water supply via base module or via laboratory supply
Technical Data:
- Pipe, PVC
- Inner diameter: 17mm
Pipe elements, PVC:
- Inner diameter: d
- Sudden contraction: from d=17 to d=9,2mm
- Sudden enlargement: from d=9,2 to d=17mm
- Segment bend: d=17mm, 90°
- Pipe angle: d=17mm, 90°
- Narrow pipe bend: d=17mm, r=40mm, 90°
- Wide pipe bend: d=17mm, r=100mm, 90°
Measuring ranges:
- Bourdon tube pressure gauge: 0...1,6bar
- Tube manometer: 0...0,03bar
Dimensions and Weight:
- LxWxH: 840x710x960mm
- Weight: approx. 32kg
Tell us about your requirement

Price:
Quantity
Select Unit
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
Additional detail
+91
Email
Other Products in 'Fluid Mechanics Lab Equipment' category
"We deal all over World but our main domestic market is South India"
 |
EDUTEK INSTRUMENTATION
All Rights Reserved.(Terms of Use) Developed and Managed by Infocom Network Private Limited. |